
This study aims to compare the actual bending strength of dental zirconia from different brands and investigate the optimal thickness for opacity. The research will involve a series of mechanical tests and optical assessments to determine the performance and aesthetic properties of various zirconia materials in dental applications.
The research is in-depth and the article is long, so please bear with me. Reading time is about 8 minutes.
In the realm of prosthetics, color stands as a paramount attribute. For decades, porcelain fused to metal (PFM) materials have dominated the field. Despite their popularity, these restorations exhibit aesthetic drawbacks, such as the visibility of metal margins, and their optical properties diverge from those of natural teeth. Consequently, over the past two decades, the introduction of new dental ceramics has sought to replicate both the mechanical strength and aesthetic appeal of natural dentition, leading to a decline in the use of PFM restorations. Zirconia, in particular, has gained widespread use in fixed prostheses and implants due to its superior mechanical and aesthetic qualities, biocompatibility, favorable soft tissue interaction, osseointegration, and longevity.
1. Properties of Zirconia
Zirconia exhibits three crystalline phases:
– Monoclinic phase (m phase)
– Tetragonal phase (t phase)
– Cubic phase (c phase)
The tetragonal phase remains stable at temperatures ranging from 1170 to 2370°C, and the addition of yttrium oxide (Y2O3) significantly enhances its strength and toughness. Therefore, 3 mol% yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (3Y-TZP) is widely recognized as a stable material for dental repairs.
However, 3Y-TZP zirconia inherently possesses a degree of opacity, resulting in single-layer zirconia-based fixed prostheses often falling short of ideal aesthetic standards. An alternative approach employs a double-layer structure, where aesthetic porcelain is layered over the high-strength zirconia core. Although this method improves translucency, it is more susceptible to failure due to layer instability and fracture. Moreover, the addition of decorative porcelain necessitates the removal of more tooth structure due to increased restoration thickness.
Efforts to enhance the translucency of zirconia include the development of second-generation zirconia, which involves:
– Reducing the concentration of alumina additives
– Employing higher sintering temperatures to reduce porosity
These modifications aim to improve translucency, yet achieving sufficient aesthetic outcomes through these processes remains challenging.

In the evolution of zirconia materials, the third generation introduces transparent substances to enhance translucency, such as:
– 4 mol% yttria partially stabilized zirconia (4Y-PSZ)
– 5 mol% yttria partially stabilized zirconia (5Y-PSZ)
These additions significantly boost the transparency of zirconia. However, concerns have been raised that zirconia with a high cubic phase content may exhibit increased susceptibility to contact-related damage, including those induced by sandblasting and grinding procedures. The most translucent 5Y-PSZ material has gained popularity for use in anterior crowns and bridges due to its aesthetic appeal. Nonetheless, research indicates a higher failure rate of over 2% within a 5-year period for anterior teeth restorations made from this material.
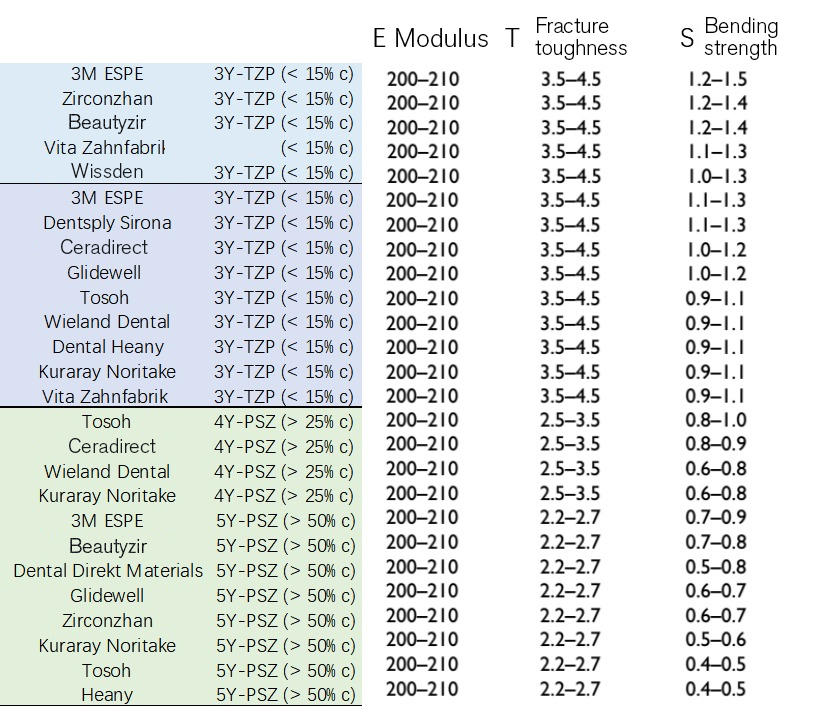
2. Composition of Zirconia Restorations and Factors Influencing Their Optical Properties
A fully assembled dental prosthesis comprises four layers, arranged from innermost to outermost:
– Substrate: natural tooth/resin core or metal core/metal base or zirconia base
– Adhesives,
– Zirconia,
– Decorative porcelain
Each of these components contributes to the final color outcome of the restoration. Moreover, the fabrication process of zirconia also plays a role in determining its color.
1. Substrate
– Zirconia exhibits a light transmittance of 20% to 50% within a 1mm thickness, classifying it as a translucent material. Consequently, the substrate can influence the color of zirconia restorations.
– Choi conducted an experiment using 0.4mm thick zirconia samples (with and without veneering ceramics) placed on four different colored substrates (white, black, gray, and tooth-colored). His findings suggest that zirconia ceramics possess a certain degree of color-masking capability, which is enhanced when veneering ceramics are applied.
– Oh emphasizes that the type of substrate is a critical factor. He evaluated six substrates, including various alloys and composite resins. His conclusion indicates that a gold alloy substrate can significantly affect the final color of zirconia restorations, whether they are 1mm or 1.5mm thick.
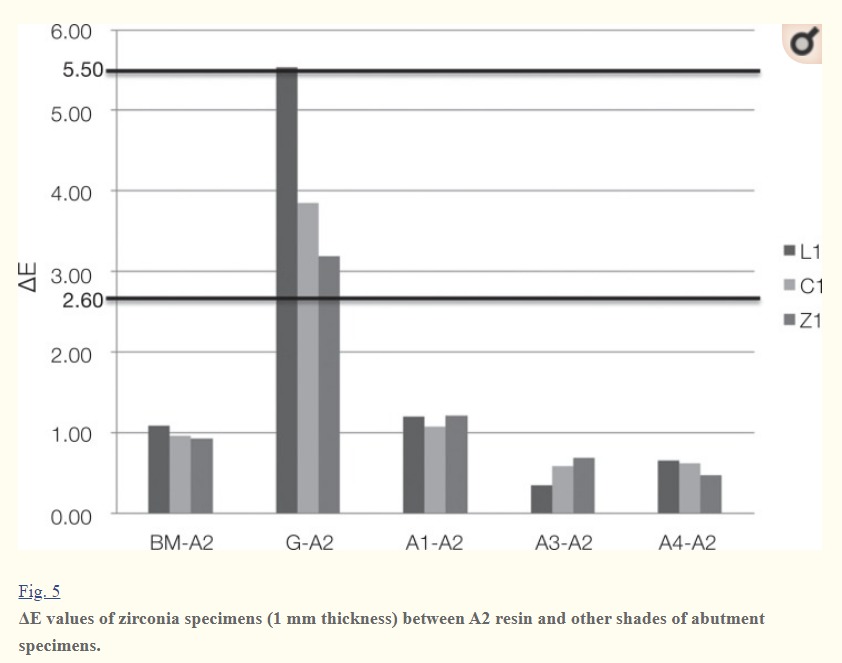
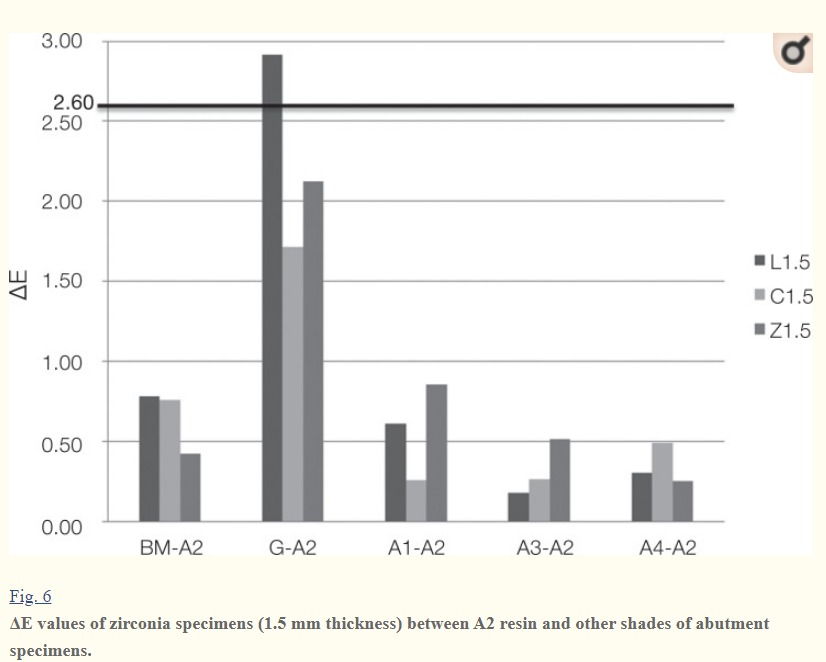
– Wang et al. assessed the total pigment (TP) of zirconia ceramics of varying thicknesses when placed on white and black substrates, observing color differences ranging from 5.5 to 15.1. This indicates the potential for color discrepancies due to the substrate, although the stark contrast between black and white backgrounds differs from the more nuanced clinical environment.
– Kim et al. investigated the impact of abutment materials on the color of the surrounding soft tissue in implant cases. Their findings revealed that zirconia abutments resulted in significantly lower average color differences compared to titanium or gold abutments, suggesting that zirconia may offer a more aesthetic outcome in such scenarios.
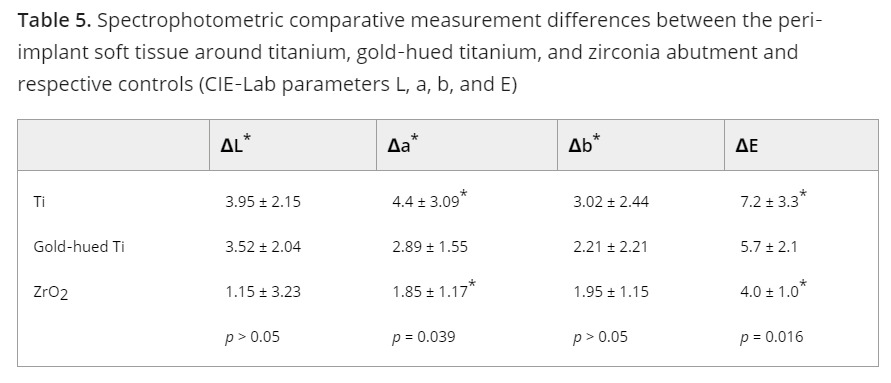
Ferrari et al. posited that when the thickness of the soft tissue is less than 2 mm, the choice of abutment material—whether zirconia or titanium—can influence the coloration of the soft tissue surrounding the implant. This suggests that the material properties of the abutment play a role in the aesthetic outcome, particularly in cases where the soft tissue is relatively thin.
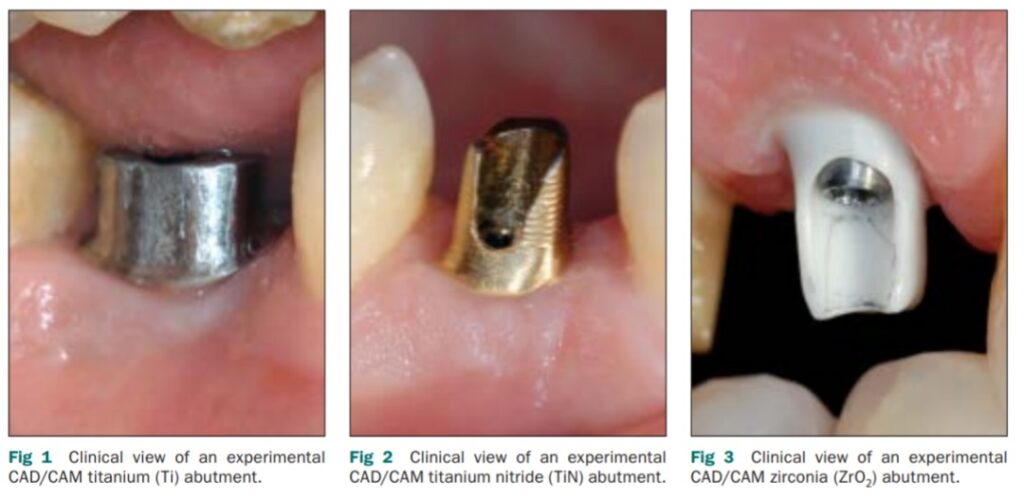
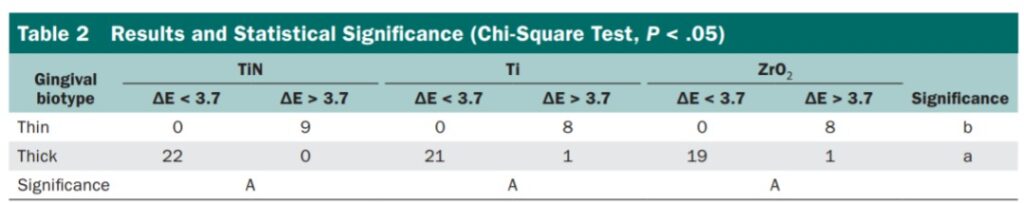
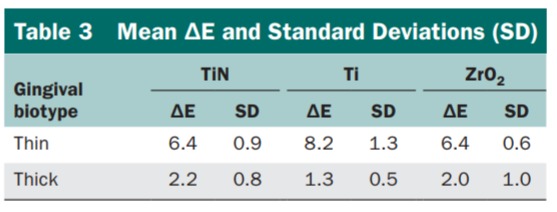
2. Adhesives
– Although the thickness of the adhesive layer is minimal, and zirconia ceramics are less transparent than feldspar and glass ceramics, adhesives still exert a minor influence on the final color of zirconia restorations. This impact, however, is less pronounced compared to that of adhesives used with glass ceramics.
– Lee et al. demonstrated that the use of opaque adhesives tends to result in a lighter final color effect, whereas transparent adhesives lead to a darker coloration. This suggests that the optical properties of adhesives can subtly alter the appearance of zirconia restorations, albeit to a lesser degree than with more translucent materials.
– Given that the bonding process is the final step in the clinical procedure for delivering prostheses, relying on adhesives for color correction is unreliable. This underscores the importance of accurate color matching prior to this stage.
– Utilizing trial paste can assist clinicians in choosing adhesives that approximate the desired color for the repair, providing a preliminary assessment of color compatibility.
3. Zirconia
– The optical properties and resulting color of zirconia restorations are influenced by various factors, including the type, brand, color, and thickness of the zirconia material.
– Zirconia exhibits optical characteristics distinct from those of human dentin, which must be considered when aiming for natural-looking restorations.
– Experimental evidence indicates that a minimum thickness of 1mm is required for zirconia to achieve an acceptable level of shading capability, ensuring that the material can effectively mimic the natural color and translucency of teeth.
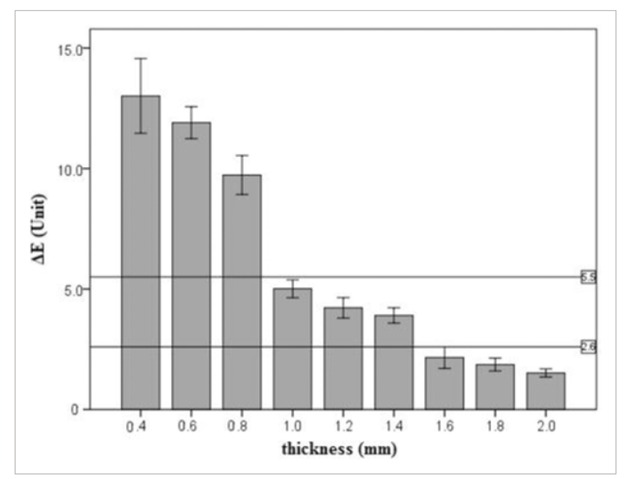
– Sinmazisik et al. conducted a study to assess the impact of varying zirconia thicknesses (0.3, 0.5, 0.7 mm) and veneering ceramic thicknesses (1 and 1.5 mm) on the color of zirconia restorations. Their findings revealed that as the thickness of zirconia increased, the L* (lightness) value also increased, while the a* (red-green axis) and b* (yellow-blue axis) values decreased. This indicates that thicker zirconia layers contribute to a lighter and potentially less chromatic appearance of the restorations, affecting their overall color balance.
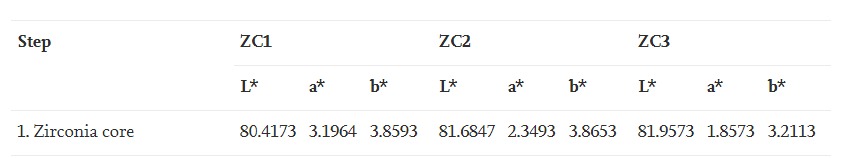
4. Decorative Porcelain
To mimic the natural appearance of teeth, zirconia is often coated with decorative ceramics that are more translucent than zirconia itself, such as feldspar ceramics, leucite, lithium disilicate, and fluorapatite glass ceramics.
There are three main techniques for applying decorative porcelain, each with distinct impacts on the restoration’s color:
– Layering
– Over pressing:
This technique involves decorating porcelain using complete anatomical technology (overpressure), resulting in the most transparent restoration with the highest color brightness. Conversely, when porcelain is decorated using cutting technology (overpressure), the restoration becomes the most opaque with the lowest brightness.
– CAD/CAM:
Offers color reproducibility comparable to traditional finishing techniques such as layering.
– The thickness of the veneering porcelain significantly influences its translucency, subsequently affecting the color reproduction capability of the restoration.
– Thickness has a greater impact on translucency than on color.
– Increasing the thickness of veneering ceramics will reduce their transparency and lead to higher a* and b* values, affecting the chromatic aspect of the restoration.
– Glazing, the final step in the manufacturing process of zirconia-based restorations, can decrease the translucency and result in a reduction of the L* value while increasing the a* and b* values, ultimately influencing the restoration’s color and appearance.
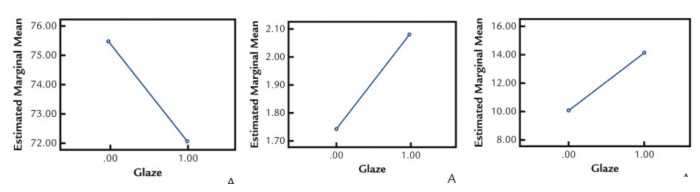
5. Processing Process
– The processing of zirconia ceramics involves several critical steps, including zirconia coloring, sintering, ceramic decoration, polishing, and glazing. Each of these stages can influence the properties of zirconia ceramics, such as particle size, density, porosity, crystal phase (monoclinic, tetragonal, cubic), and metal oxide content. These factors, in turn, significantly affect the optical properties of zirconia:
– Reducing the grain size of zirconia particles enhances transparency, as smaller grains allow for better light transmission.
– A low porosity level, both in terms of pore size and content, contributes to improved transparency in ceramics, as fewer and smaller pores minimize light scattering.
– An increase in the content of zirconia in the cubic phase can also enhance transparency, as this phase is more transparent than the monoclinic and tetragonal phases.
These processing factors are crucial in achieving the desired optical properties and color effects in zirconia-based restorations, ensuring they closely resemble natural teeth.
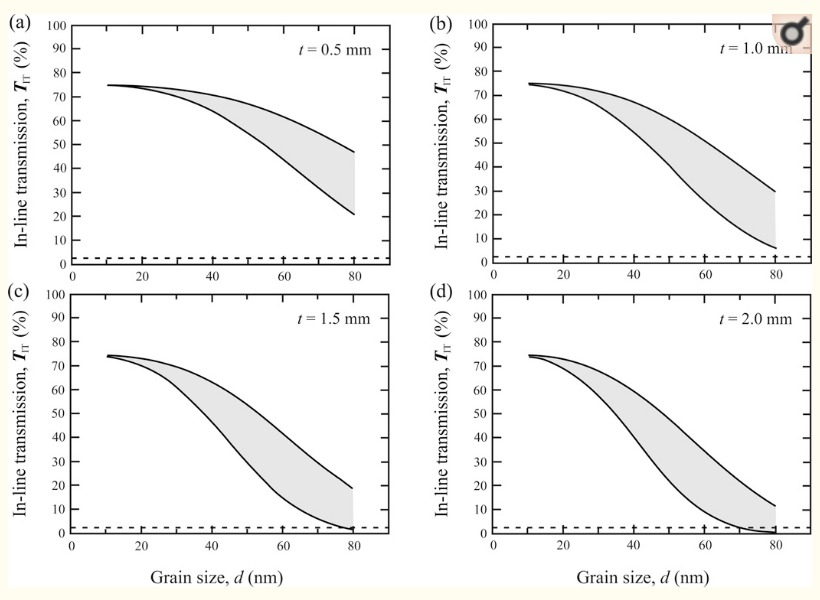
– Coloring:
There are three primary techniques employed to color zirconia:
◇ Pre-coloring zirconia powder to create pre-colored zirconia ceramics. However, these pre-colored materials often require additional coloring as they typically exhibit high L* (lightness) values and low a* and b* (chromaticity) values.
◇ Coloring unsintered zirconia by immersing it in a coloring solution, which allows for direct pigmentation before the sintering process.
◇ Coloring sintered zirconia with a colorant, which is applied after the sintering process to adjust the color of the already hardened material.
– Sintering:
Zirconia is typically sintered in a sintering furnace, undergoing a temperature cycle that lasts 12 hours, reaching a final temperature between 1400 to 1550 °C. It has been observed that controlling the final sintering temperature within the range of 1450 to 1500 °C can enhance the translucency of zirconia. However, to maintain the necessary bending strength of the material, the sintering temperature should not exceed 1550 °C. This balance between translucency and mechanical strength is crucial in the fabrication of zirconia-based dental restorations.
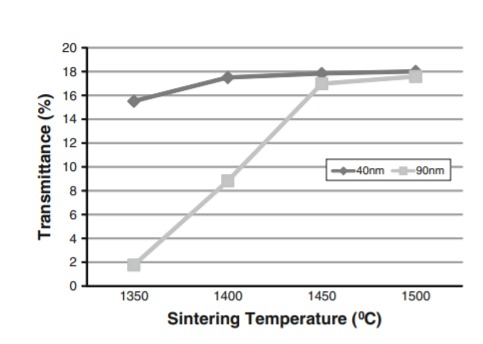
C (Source: Reference 13)
3. Summary
– While zirconia restorations generally offer superior aesthetics compared to porcelain restorations, achieving a perfect color match with natural teeth remains challenging due to the multitude of factors influencing the final color of zirconia-based restorations.
– Although the aesthetic impact of each factor is acknowledged, there are currently no established practical clinical guidelines to optimize color reproduction. Consequently, further research is essential, particularly focusing on developing clinical guidelines for various factors such as the minimum thickness of zirconia, the minimum thickness of veneering ceramics, and the optimal thickness ratio between zirconia and veneering ceramics.
– In the fabrication and clinical application of prostheses, the use of electronic colorimeters or spectrophotometers can be instrumental in identifying and rectifying potential color mismatch issues, ensuring a more accurate color match with the patient’s natural teeth.
This comprehensive understanding and application of the factors affecting zirconia coloration are crucial for advancing the field of dental aesthetics and improving patient satisfaction with their restorations.
END
reference:
1. Yoshinari M. Future prospects of zirconia for oral implants -A review. Dental materials journal. Jan 31 2020; 39(1):37-45.
2. Miyazaki T, Nakamura T, Matsumura H, Ban S, Kobayashi T. Current status of zirconia restoration. Journal of prosthodontic research. Oct 2013; 57(4):236-261.
3. Zhang Y, Lawn BR. Novel Zirconia Materials in Dentistry. Journal of dental research. Feb 2018; 97(2):140-147.
4. Oh SH, Kim SG: Effect of abutment shade, ceramic thickness, and coping type on the final shade of zirconia all-ceramic restorations: in vitro study of color masking ability. J Adv Prosthodont 2015; 7:368-374 5. Kim A, Campbell SD, Viana MA, et al: Abutment material effect on peri-implant soft tissue color and perceived esthetics. J Prosthodont 2016; 25:634-640 6. Ferrari M, Carrabba M, Vichi A, et al: Influence of abutment color and mucosal thickness on soft tissue color. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2017; 32:393-399 7. Lee YK, Cha HS, Ahn JS: Layered color of all-ceramic core and veneer ceramics. J Prosthet Dent 2007; 97:279-286 8. Tabatabaian F, Dalirani S, Namdari M: Effect of thickness of zirconia ceramic on its masking ability: an in vitro study. J Prosthodont 2017 Apr 28. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.12625.
9. Sinmazisik G, Demirbas B, Tarcin B: Influence of dentin and core porcelain thickness on the color of fully sintered zirconia ceramic restorations. J Prosthet Dent 2014; 111:142-149 10. Tabatabaian, Farhad. Color in Zirconia-Based Restorations and Related Factors: A Literature Review[J]. Journal of Prosthodontics, 2018.
11. Sravanthi Y, Ramani YV, Rathod AM, et al: The comparative evaluation of the translucency of crowns fabricated with three different all-ceramic materials: an in vitro study. J Clin Diagn Res 2015; 9:ZC30-34 12. Vagkopoulou T, Koutayas SO, Koidis P, et al: Zirconia in dentistry: Part 1. Discovering the nature of an upcoming bioceramic. Eur J Esthet Dent 2009; 4:130-151 13. Stawarczyk B, Ozcan M, Hallmann L, et al: The effect of zirconia sintering temperature on flexural strength, grain size, and contrast ratio. Clin Oral Investig 2013; 17:269-274 14. Sivaraman K, Chopra A, Narayan AI, Balakrishnan D. Is zirconia a viable alternative to titanium for oral implant? A critical review. Journal of prosthodontic research. Apr 2018; 62(2):121-133.
15. Osman RB, Swain MV. A Critical Review of Dental Implant Materials with an Emphasis on Titanium versus Zirconia. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). Mar 5 2015; 8(3):932-958.
16. Roehling S, Schlegel KA, Woelfler H, Gahlert M. Zirconia compared to titanium dental implants in preclinical studies-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical oral implants research. May 2019; 30(5):365-395.
17. Lundberg K, Wu L, Papia E. The effect of grinding and/or airborne-particle abrasion on the bond strength between zirconia and veneering porcelain: a systematic review. Acta biomaterialia odontologica Scandinavica. Jan 2017; 3(1):8-20.
18. Denry I, Kelly JR. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dental materials : official publication of the Academy of Dental Materials. Mar 2008; 24(3):299-307.
19. Zarone F, Di Mauro MI, Ausiello P, Ruggiero G, Sorrentino R. Current status on lithium disilicate and zirconia: a narrative review. BMC oral health. Jul 4 2019; 19(1):134.




Comments (1)
Rashad Guillotsays:
07/26/2024 at 5:48 PMYour passion for your subject matter shines through in every post It’s clear that you genuinely care about sharing knowledge and making a positive impact on your readers Kudos to you!