Understanding the Use of Zirconia in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of modern dentistry, materials science has revolutionized the way dental professionals approach restorative and cosmetic procedures. Among the myriad of materials available, zirconia has emerged as a standout choice for its exceptional properties. This article delves into the use of zirconia in dentistry, exploring its benefits, applications, and the techniques involved in its utilization.
What is Zirconia?
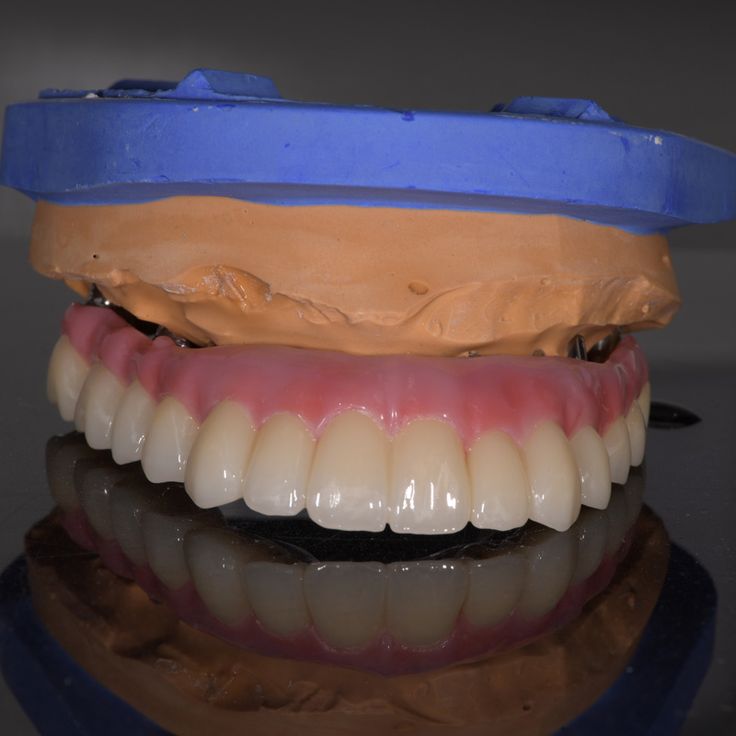
Zirconia, or zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), is a crystalline oxide of zirconium. It is a ceramic material that boasts remarkable strength, durability, and biocompatibility, making it an ideal candidate for dental applications. Zirconia is often used in the fabrication of dental crowns, bridges, implants, and other prosthetic devices.
Advantages of Zirconia in Dentistry
- Strength and Durability: Zirconia is renowned for its high fracture toughness and resistance to wear, which translates to long-lasting dental restorations.
- Aesthetics: Zirconia can be manufactured to closely mimic the natural translucency and color of teeth, providing a highly aesthetic result.
- Biocompatibility: Being a bioinert material, zirconia is well-tolerated by the human body, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or adverse tissue responses.
- Minimal Tooth Preparation: Due to its strength, zirconia restorations often require less removal of the natural tooth structure compared to other materials.
- Corrosion Resistance: Zirconia is resistant to corrosion, ensuring that the restorations maintain their integrity over time.
Applications of Zirconia in Dentistry
- Dental Crowns: Zirconia crowns are used to restore the function and appearance of damaged or decayed teeth. They are particularly suitable for posterior teeth due to their strength.
- Bridges: Zirconia bridges can replace missing teeth, providing a stable and aesthetic solution.
- Implants: Zirconia implants are an alternative to titanium implants, offering a metal-free option for patients with metal sensitivities.
- Inlays and Onlays: These are used to restore teeth with moderate decay or damage, providing a conservative yet durable solution.
The Process of Using Zirconia in Dental Restorations
- Consultation and Planning: The dentist evaluates the patient’s oral health and discusses the treatment options, including the use of zirconia.
- Tooth Preparation: The affected tooth is prepared by removing decay and shaping it to accommodate the zirconia restoration.
- Impression Taking: An impression of the prepared tooth is taken to create a precise model for the zirconia restoration.
- Fabrication: Using CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology, the zirconia restoration is designed and milled to exact specifications.
- Try-In and Adjustment: The zirconia restoration is tried in the patient’s mouth to ensure proper fit and aesthetics. Adjustments are made as necessary.
- Cementation: Once the fit is confirmed, the zirconia restoration is permanently cemented in place.
Conclusion
Zirconia has become a cornerstone material in modern dentistry, offering a blend of strength, aesthetics, and biocompatibility that is hard to match. Its applications in crowns, bridges, implants, and other restorations have provided patients with durable and natural-looking solutions to their dental needs. As technology continues to advance, the use of zirconia in dentistry is likely to expand, further enhancing the quality of dental care.
For those considering dental restorations, consulting with a dental professional about the potential use of zirconia can lead to informed decisions and successful outcomes. Remember, a healthy smile is not just about aesthetics; it’s about the strength and longevity of the materials that support it.




Leave a Reply